Mock API Example
This example shows you how to use Mock Service Worker and the native fetch API. It builds out a mock API on the frontend to consume data without needing to rely on a backend system. This allows developers to use mock endpoints for testing while backend APIs are developed. Later, mock endpoints can easily be swapped out for production endpoints.
This example does not include any backend persistence via IndexedDB. This is out of scope for this example. Instead, this example provides two simplified endpoints to call:
[GET] /speciesreturns a list of 4 species.[POST] /speciesreturns the original list, with an additional species added (this is hard coded for simplicity).
Learn more about RADFish examples at the official documentation. Refer to the RADFish GitHub repo for more information and code samples.
Preview
This example will render as shown in this screenshot:
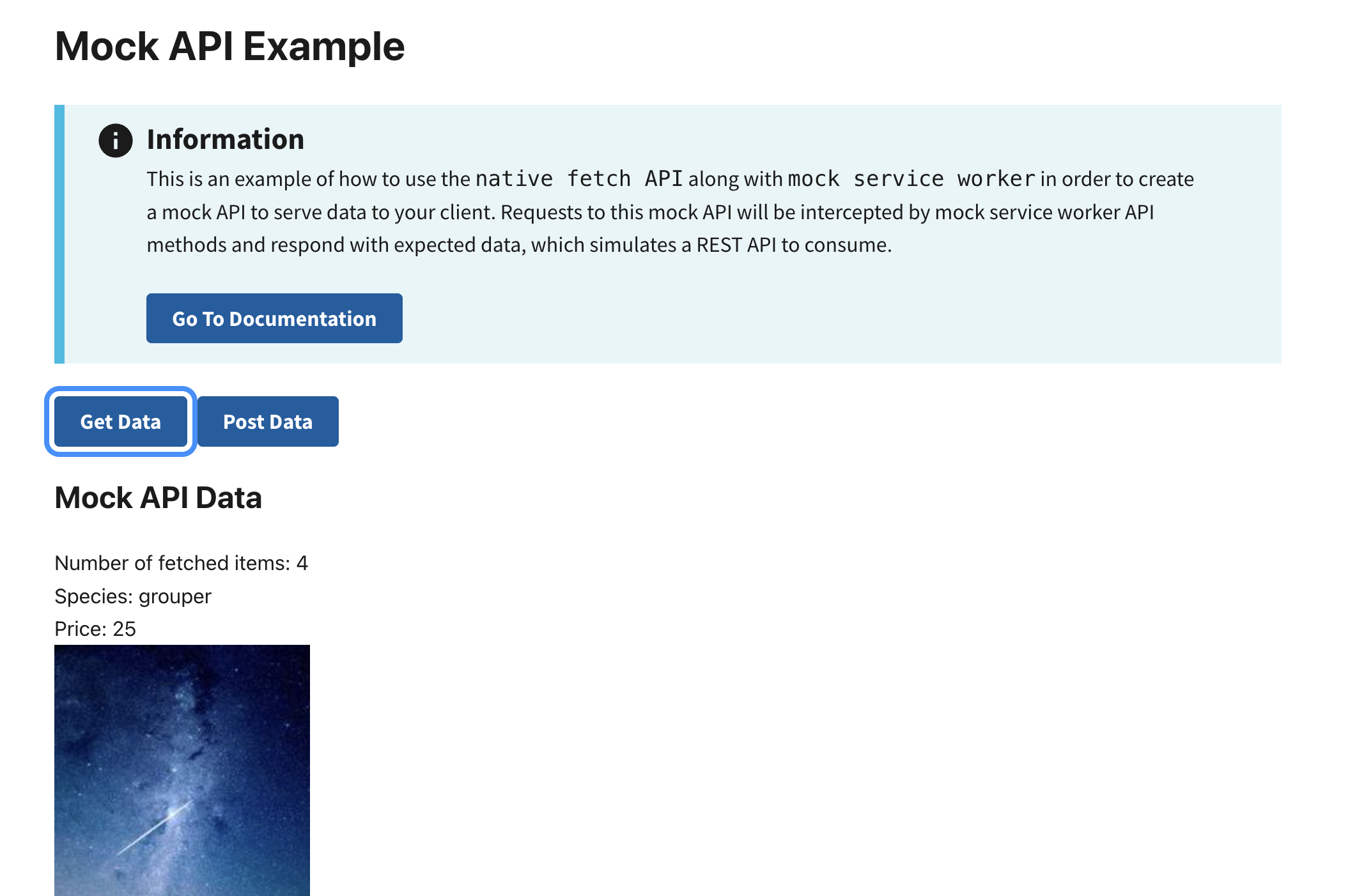
Steps
1. Enable Mocking in index.jsx
In the index.jsx file, enable mocking from the mock service worker. This ensures that your mock API is being called while in development.
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom/client";
import "./styles/theme.css";
import App from "./App";
// Enable the mock service worker
async function enableMocking() {
const { worker } = await import("./mocks/browser");
const onUnhandledRequest = "bypass"; // Ignore unhandled requests to prevent errors in development
if (import.meta.env.MODE === "development") {
return worker.start({
onUnhandledRequest,
serviceWorker: {
url: `/mockServiceWorker.js`, // Path to the mock service worker
},
});
}
// For non-development environments, fallback to a different service worker
return worker.start({
onUnhandledRequest,
serviceWorker: {
url: `/service-worker.js`,
},
});
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
enableMocking().then(() => {
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>,
);
});
Key Points:
- Ensure the
mockServiceWorker.jsfile is present in thesrcdirectory. - This setup dynamically starts the service worker based on the environment.
2. Create the Mocks Directory
- Create a
mocksdirectory insrc. - Create
browser.jsandhandlers.jsfiles.
3. Define Mock Endpoints in browser.js
The browser.js file will import the endpoints configured in the handlers.js file. It wraps them in a higher order function from the msw/browser library. This sets up mock endpoints and intercepts them when getting called from the client:
// src/mocks/browser.js
import { setupWorker } from "msw/browser";
import { handlers } from "./handlers";
// Configure the mock service worker with the handlers
export const worker = setupWorker(...handlers);
Explanation:
setupWorkerinitializes the service worker.- Spread the
handlersarray to register mock endpoints.
4. Configure Endpoints in handlers.js
You can setup any endpoints that you want to mock within handlers.js. Be sure to export these handlers so that they can be imported into browser.js appropriately:
import { http, HttpResponse } from "msw";
export const MSW_ENDPOINT = {
SPECIES: "/species", // Endpoint for fetching fish species
};
export const species = [
{ name: "grouper", price: 25.0, src: "./sample-img.jpg" },
{ name: "salmon", price: 58.0, src: "./sample-img.jpg" },
{ name: "marlin", price: 100.0, src: "./sample-img.jpg" },
{ name: "mahimahi", price: 44.0, src: "./sample-img.jpg" },
];
// Mock API handlers
export const handlers = [
// GET endpoint: Fetch list of species
// This implementation can/should change depending on your needs
http.get(MSW_ENDPOINT.SPECIES, () => {
return HttpResponse.json(
{
data: species,
},
{ status: 200 },
);
}),
// POST endpoint: Add a new species
// In a full stack implementation, there will likely be some logic on the server to handle/store persistent data
http.post(MSW_ENDPOINT.SPECIES, async ({ request }) => {
const requestData = await request.json();
const response = [requestData.data, ...species];
return HttpResponse.json({ data: response }, { status: 201 });
}),
];
5. Access Mock Endpoints with Fetch
You can now use these endpoints in your application by making HTTP requests with the native fetch API.
GET Request Example
Fetch the list of fish species:
import { MSW_ENDPOINT } from "./mocks/handlers";
const getRequestWithFetch = async (endpoint) => {
try {
const response = await fetch(`${endpoint}`, {
headers: {
"X-Access-Token": "your-access-token",
},
});
if (!response.ok) {
const error = await response.json();
return error;
}
const data = await response.json();
return data;
} catch (err) {
const error = `[GET]: Error fetching data: ${err}`;
return error;
}
};
// [GET] /species
const { data } = await getRequestWithFetch(MSW_ENDPOINT.SPECIES);
POST Request Example
Add a new species to the mock database:
const postRequestWithFetch = async (endpoint, submittedData) => {
try {
const response = await fetch(endpoint, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-Access-Token": "your-access-token",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
...submittedData,
}),
});
if (!response.ok) {
const error = await response.json();
return error;
}
const data = await response.json();
return data;
} catch (err) {
const error = `[GET]: Error fetching data: ${err}`;
return error;
}
};
// [POST] /species
const { data } = await postRequestWithFetch(MSW_ENDPOINT.SPECIES, {
data: {
name: "tuna",
price: 75,
src: "./sample-img.jpg",
},
});