Computed Form Fields Example
This example shows you how to build a form with computed form fields. Computed form fields automatically calculate a value based on a separate read-only field. For example, if a user inputs a quantity, a computed form field can multiply that number by a price to give a total cost.
Learn more about RADFish examples at the official documentation. Refer to the RADFish GitHub repo for more information and code samples.
Preview
This example will render as shown in this screenshot:
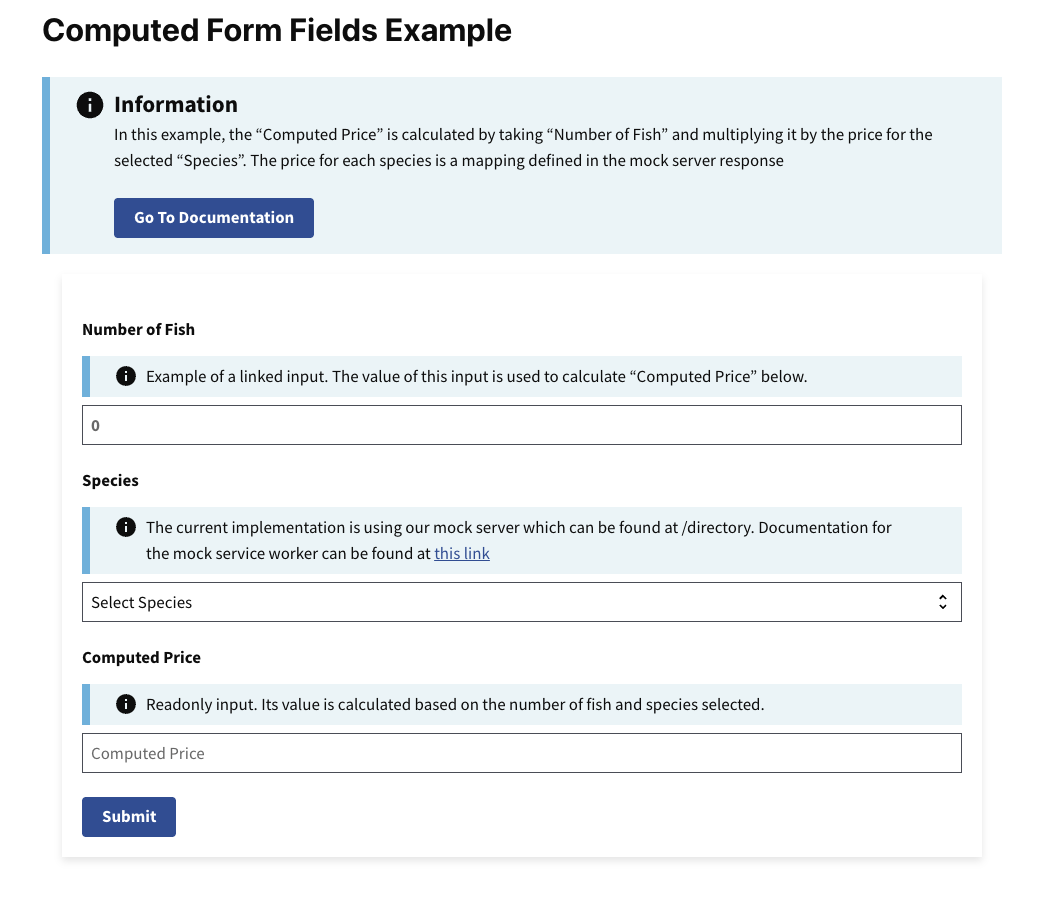
Steps
1. Define Constants for Input Fields
Before building out your form, define constants for each input field. Using constants helps reduce errors and makes your logic more maintainable.
const SPECIES = "species";
const NUMBER_OF_FISH = "numberOfFish";
const COMPUTED_PRICE = "computedPrice";
In this example, we will build a form with three inputs. The values from the first two inputs will compute the value of computedPrice.
2. Initialize the Form Component with State
Next, we'll define the main form component. To manage the data entered in the form, we initialize it with a formData state variable, which is an empty object. This state will dynamically store the values of the form fields as users interact with the form.
The setFormData function allows us to update the state whenever an input changes. This ensures the form data is kept in sync.
const ComputedForm = () => {
const [formData, setFormData] = useState({});
return (
// form JSX will go here
);
};
3. Structuring the Form with Inputs
In the return statement of the component, use the Trussworks Form component to structure your form. Within the form, include input components such as TextInput, referencing the variables defined in Step 1 (e.g. NUMBER_OF_FISH) instead of hardcoding strings. This practice helps avoid typos and ensures consistency when accessing the formData state. For better organization and styling, wrap your inputs within the FormGroup component provided by Trussworks.
return (
<Form
onSubmit={handleSubmit}
className="maxw-full margin-205 padding-205 bg-white radius-8px shadow-2"
>
<FormGroup>
<Label className="text-bold" htmlFor={NUMBER_OF_FISH}>
Number of Fish
</Label>
<TextInput
className="text-bold"
id={NUMBER_OF_FISH}
name={NUMBER_OF_FISH}
type="number"
placeholder="0"
value={formData[NUMBER_OF_FISH] || ""}
/>
4. Adding Input Handlers for Form Fields
Use handleNumberFishChange and handleSelectChange to manage the state for the Number of Fish and Species fields. These functions update the formData state whenever the user interacts with the inputs.
For the Number of Fish input, the handleNumberFishChange function captures the input value and updates the corresponding field in the formData state. Similarly, the handleSelectChange function updates the state when the user selects a species.
This function handles changes in the Number of Fish input field:
const handleNumberFishChange = (event, formData) => {
const { value } = event.target;
setFormData({
...formData, // Preserve existing form data
[NUMBER_OF_FISH]: value, // Update the "Number of Fish" field
});
};
Use the handleNumberFishChange function to manage the Number of Fish input:
<TextInput
className="text-bold"
id={NUMBER_OF_FISH}
name={NUMBER_OF_FISH}
type="number"
placeholder="0"
value={formData[NUMBER_OF_FISH] || ""} // Display the current state value
onChange={(event) => handleNumberFishChange(event, formData)} // Trigger the handler on change
/>
5. Calculating Computed Price
In addition to updating the input value of numberOfFish, we also want to update the value of computedPrice. We can do that by adding a helper function to run some logic to compute that value. We then call that helper function in the input's onChange handler:
This maps species to their respective prices:
const speciesPriceMap = {
grouper: 25.0,
salmon: 58.0,
marlin: 100.0,
mahimahi: 44.0,
};
This function is kept outside the component since it doesn't rely on React state or lifecycle:
const computeFieldValue = (numberOfFish, species) => {
let computedPrice = parseInt(numberOfFish || 0) * parseInt(speciesPriceMap[species] || 0);
return computedPrice.toString();
};
This function updates the Number of Fish and dynamically computes the "Computed Price":
const handleNumberFishChange = (event, formData) => {
const { value } = event.target;
setFormData({
...formData,
[NUMBER_OF_FISH]: value,
[COMPUTED_PRICE]: computeFieldValue(value, formData?.species || ""), // Compute and update the "Computed Price"
});
};