On-Device Storage Example
This example demonstrates how to use RADFish's storage system with IndexedDB for on-device data persistence. It showcases the Application and Collection patterns for managing structured data with schema validation.
Key RADFish Concepts
- Application Instance: Configured with stores and collections
- Schema-based Storage: Type-safe data validation
- Collection API: Consistent CRUD operations
- IndexedDB Integration: Automatic persistence with offline support
Use cases include:
- Offline on-device data storage (most cases)
- Local non-relational database (online or offline use)
- Form data persistence across sessions
- Structured data with validation
Learn more about RADFish examples at the official documentation. Refer to the RADFish GitHub repo for more information and code samples.
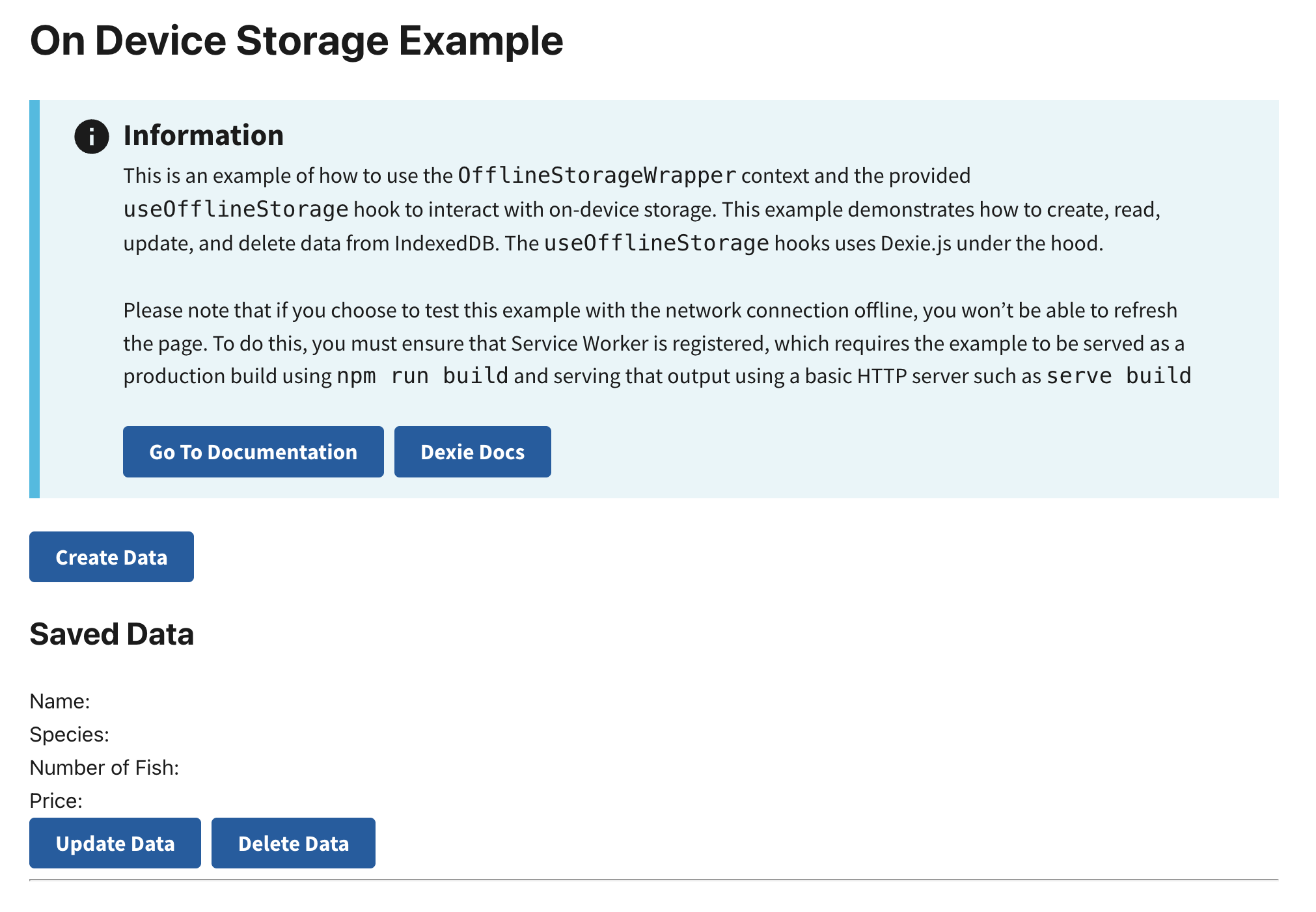
Preview
This example will render as shown in this screenshot:
Steps
1. Configure RADFish Application with Schema
In the index.jsx file, define your Application with stores and schemas:
import { Application } from "@nmfs-radfish/radfish";
import { IndexedDBConnector } from "@nmfs-radfish/radfish/storage";
const app = new Application({
stores: {
fishingData: {
connector: new IndexedDBConnector("on-device-storage-app"),
collections: {
formData: {
schema: {
fields: {
id: { type: "string", primaryKey: true },
fullName: { type: "string" },
email: { type: "string" },
phoneNumber: { type: "string" },
numberOfFish: { type: "number" },
species: { type: "string" },
computedPrice: { type: "number" },
isDraft: { type: "boolean" },
},
},
},
species: {
schema: {
fields: {
id: { type: "string", primaryKey: true },
name: { type: "string" },
price: { type: "number" },
},
},
},
},
},
},
});
Key schema concepts:
- Primary Key: Each collection must have a field marked as
primaryKey: true - Field Types: Ensures data validation (string, number, boolean)
- Multiple Collections: Organize related data in separate collections
2. Initialize and Provide the Application Instance
The Application waits for stores to be ready before rendering:
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
app.on("ready", () => {
root.render(
<ErrorBoundary>
<React.StrictMode>
<App application={app} />
</React.StrictMode>
</ErrorBoundary>,
);
});
The App component wraps children with the Application context provider:
const App = ({ application }) => {
return (
<Application application={application}>
<div className="App grid-container">
<Router>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<HomePage />} />
</Routes>
</Router>
</div>
</Application>
);
};
Using Collections in Components
Access Collections with useApplication Hook
In any component within the Application context, access collections using the useApplication hook:
import { useApplication } from "@nmfs-radfish/react-radfish";
const HomePage = () => {
const application = useApplication();
const formDataCollection = application.stores.fishingData.getCollection("formData");
// Use collection methods...
};
Collection API Methods
Collections provide the following methods for data operations:
Create
const newData = {
id: crypto.randomUUID(),
fullName: "John Doe",
species: "Tuna",
numberOfFish: 3,
computedPrice: 150,
isDraft: false
};
await formDataCollection.create(newData);
Find
// Find all records
const allData = await formDataCollection.find();
// Find with criteria
const draftRecords = await formDataCollection.find({ isDraft: true });
Update
const updatedData = {
id: "existing-id",
fullName: "Jane Doe",
numberOfFish: 5,
// ... other fields
};
await formDataCollection.update(updatedData);
Delete
// Delete by ID
await formDataCollection.delete({ id: "record-id" });
All methods are type-safe and validate data against the schema defined in your Application configuration.